Nous avons des traitements non chirurgicaux pour les patients de tous âges. Notre signature est notre excellent service et nos résultats magnifiquement naturels.
Evaluation de vos besoins en esthétique avec un professionnel en médecine esthétique ayant une formation agréée par le Collège des Médecins du Québec.
Traitement par un médecin ayant la maîtrise des techniques d’injection de pointe.
Suivi rassurant en clinique de médecine esthétique.


Depuis 1990 nous utilisons la toxine botulique pour atténuer les rides d’expressions en relaxant temporairement certains muscles du visage. Cette toxine aurait également un effet direct sur les fibroblastes, celle-ci étant responsable de la production de collagène et de ce fait un effet stabilisant sur les rides et la qualité de la peau.
Les effets cliniques apparaissent 24-72 heures après injection et dure de 5 à 7 mois.
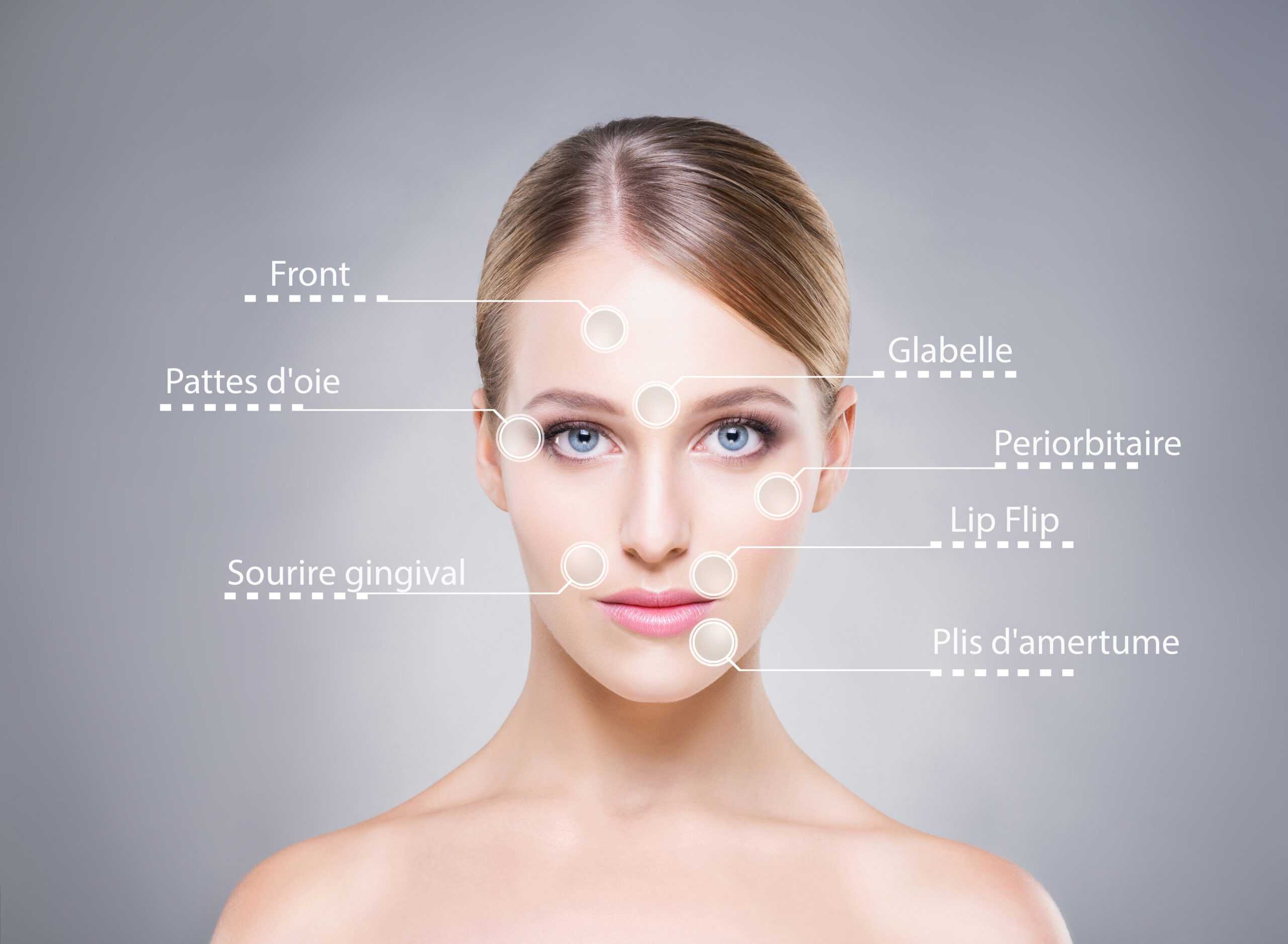
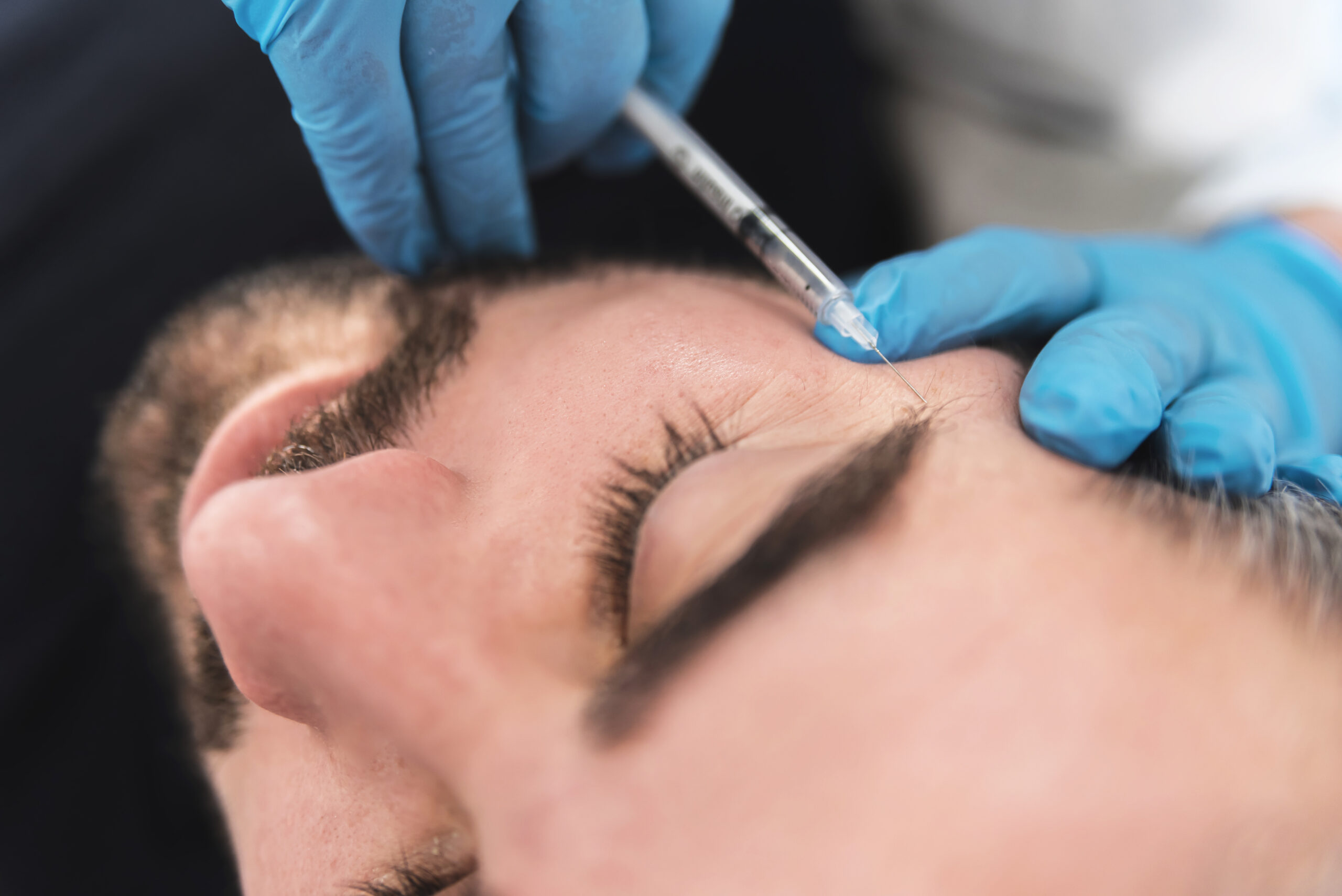

Cette technique cible les fines ridules surtout autour des yeux et de la lèvre supérieure, les taches pigmentaires et les fines cicatrices que notre peau affronte avec le temps.

En effet l’acide hyaluronique et l’agent de comblement parfait car il est non immunogène, peu allergisant, réversible, reproductible, durable (de 8 à 12 mois).
A être injecté de préférence par un médecin expérimenté.

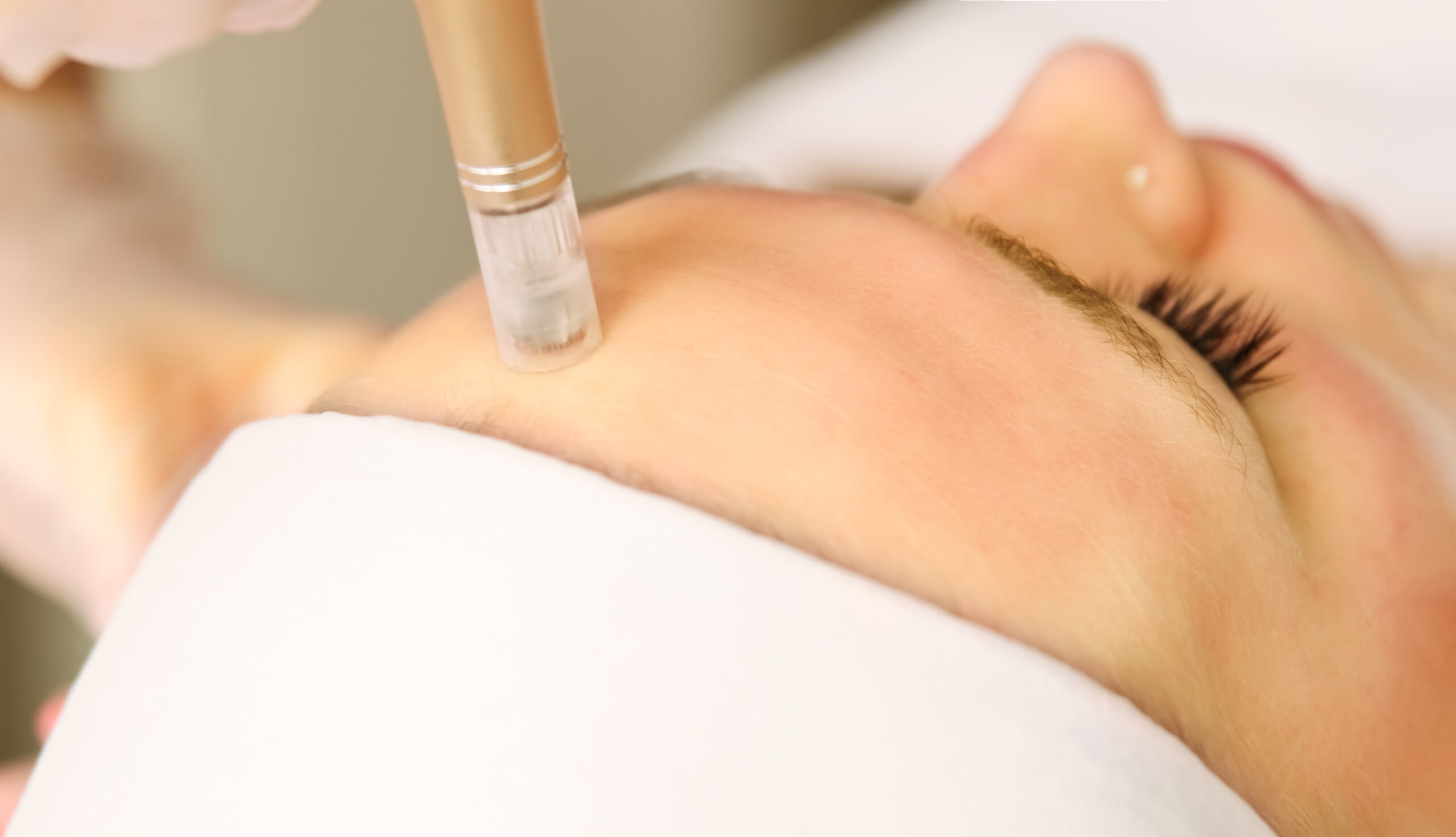
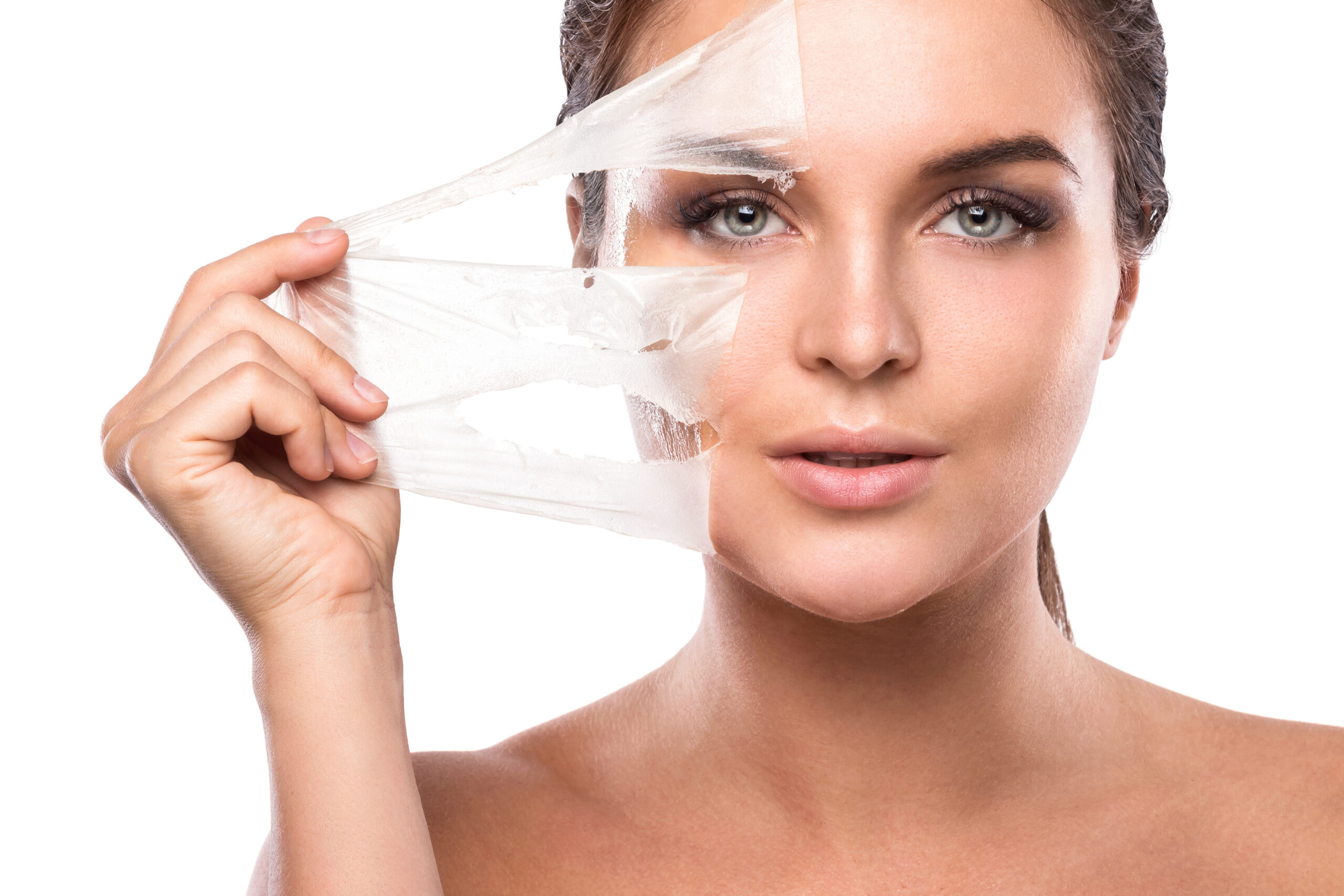
Sans douleur, délivrance de vitamines, d’acide hyaluronique non réticulé afin de le nourrir, de l’hydrater.
Ultimement la peau sera régénérée.
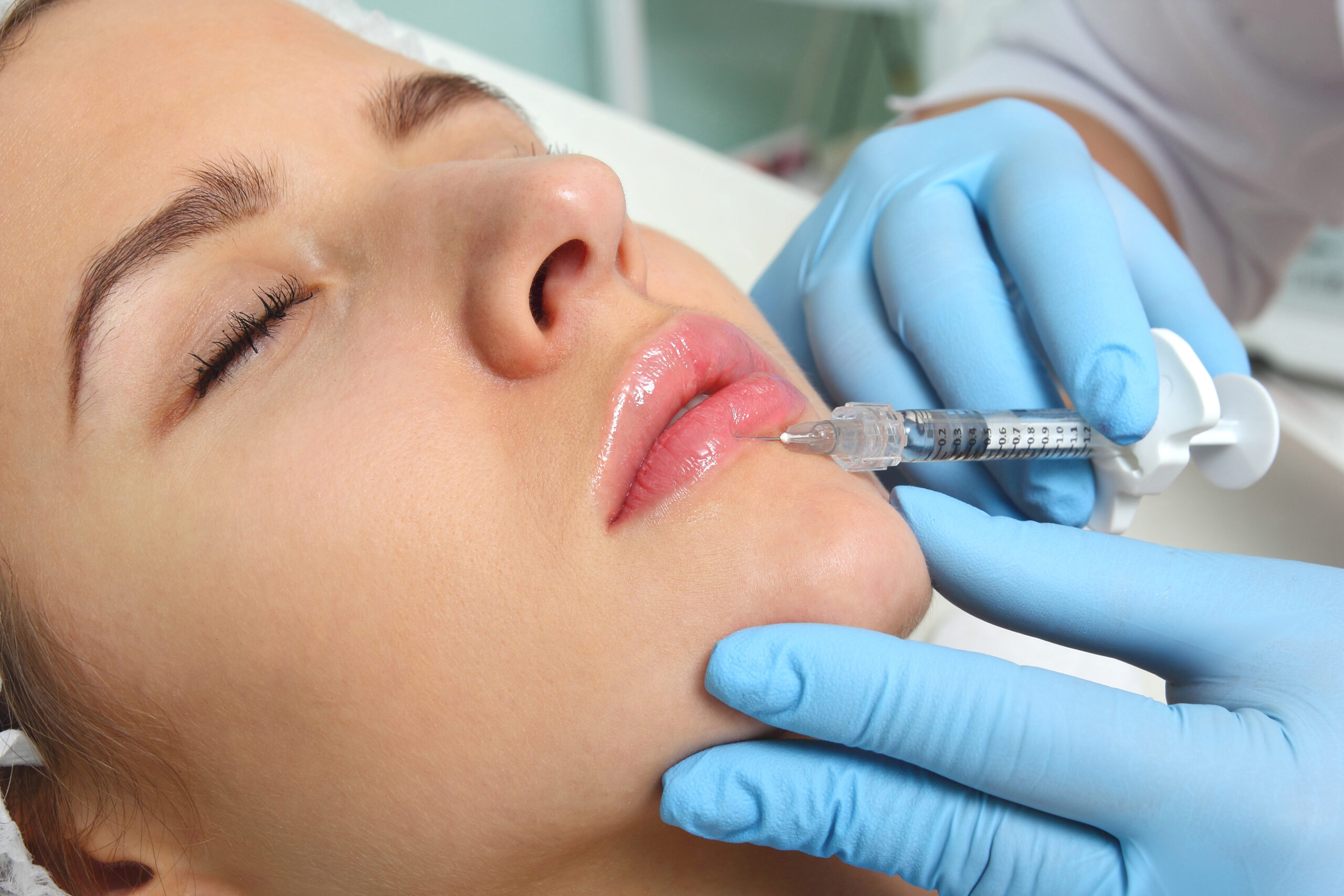
Alternative au comblement avec acide hyaluronique des lèvres.
Le lip flip donnera un look pulpeux à votre lèvre supérieure qui durera trois mois.

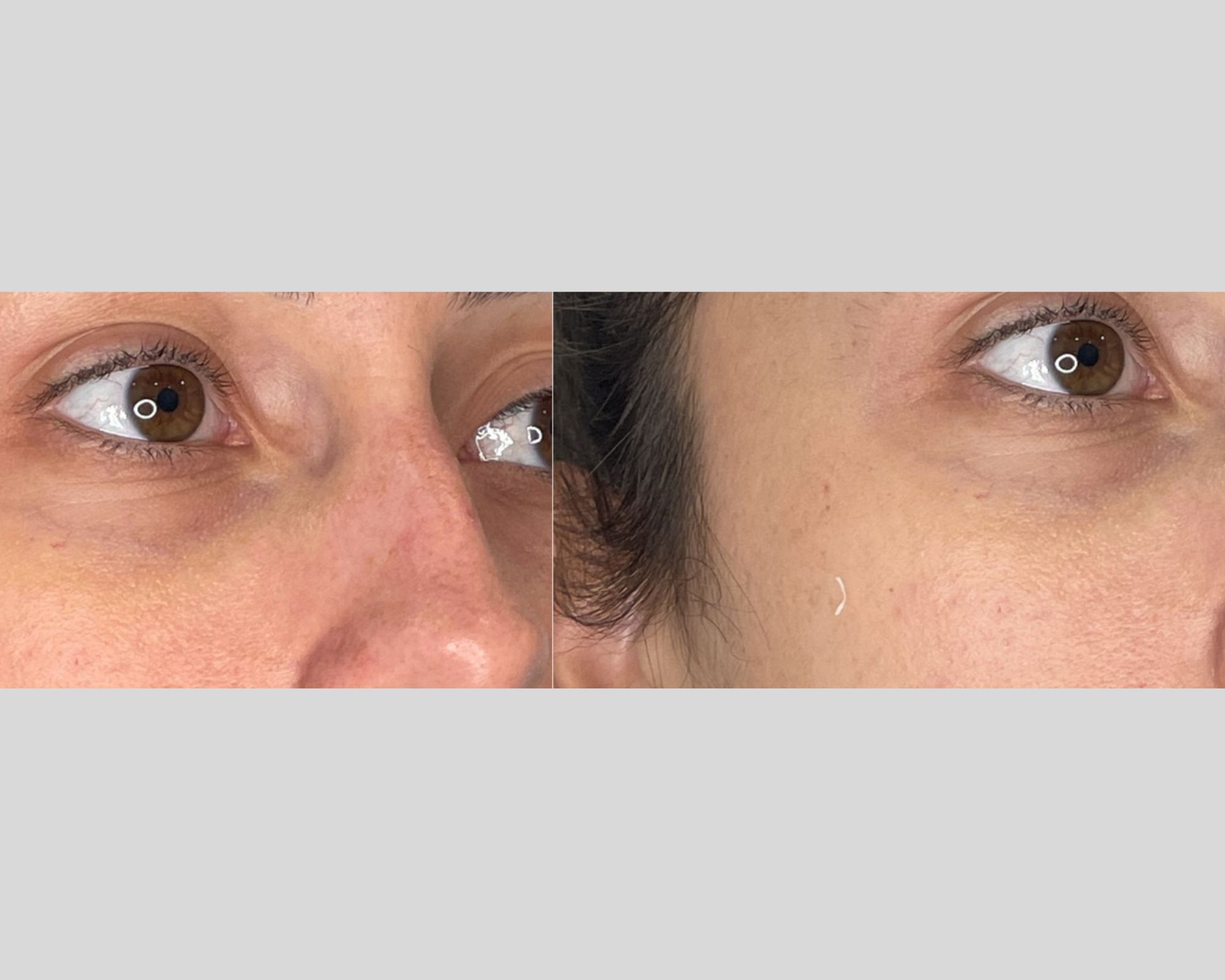
Peut également être associée à la fatigue, la déshydratation, rarement à des conditions médicales, et souvent génétique.
Correction de la zone avec acide hyaluronique et microneedling.

Docteur en médecine (Université de Montréal 1988), Université de Lille, France, Université de Sherbrooke, UCL Louvain, Belgique.
Spécialiste en médecine familiale.
Chercheur associé en dermatologie clinique , centre de recherche SIMA, Montréal, Canada
Membre :
Canadian Association of Aesthetic Medicine
Société Belge de Médecine Esthétique
Société Internationale Multidisciplinaire en Médecine Régénérative.
Président de la Société Canadienne de Médecine Régénérative.
Conférencier en Médecine Régénérative.
Formateur en médecine esthétique : neuromodulateur, agents de comblement, microneedling.
Infirmière
Dr Sakellarides.”
Merci docteur.”
Lip Flip
Avertissement : Ces photos sont publiées à titre indicatif afin de fournir de l’information sur la nature de l’intervention. Elles ne constituent aucunement une garantie de résultat et proviennent de notre système de gestion des photos des dossiers patients.
© 2025 Clinique Esthétique MD.